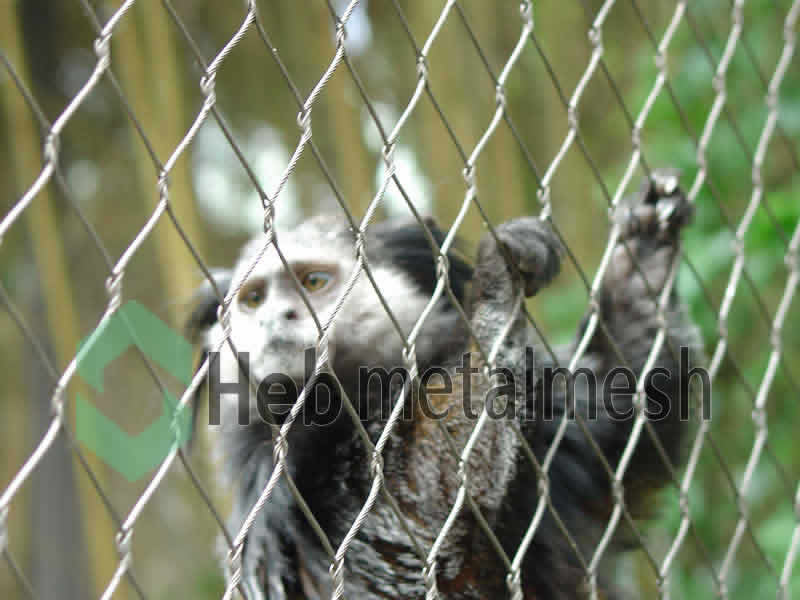
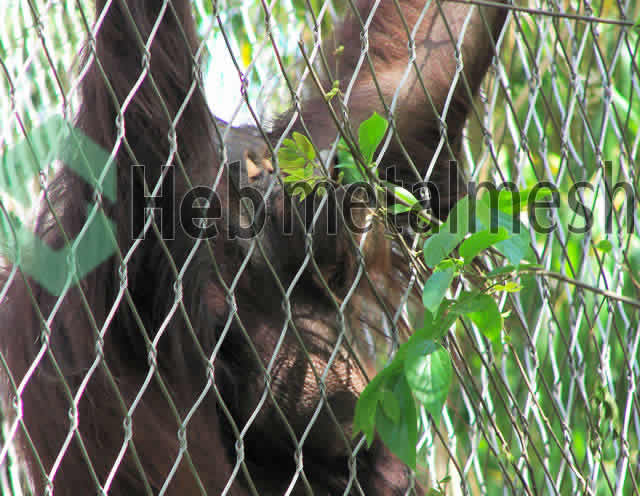
We utilizes pure handmade technology in producing stainless steel rope mesh for various zoo applications. All its mesh products are free from rusts and contaminations and can contribute to the formation of solid animal barrier netting. No matter whether the animals are carnivorous or herbivorous, once these stainless steel mesh ropes are properly installed in the cages then it is impossible for them to break or tear it using teeth, paws or horns. All its products are manufactured under the supervision of experienced craftsmen who paid essential importance to details. As a result these are also ideal for making secured bird aviary netting, animal enclosure mesh.
About Stainless steel mesh for lion enclosure, lion cages, lion barrier nets – 100% Hand Woven, Strong, Flexible, Soft, Durable, No Rust, No Corrosion, Useful Life Over 30 Years
Pliable, transparent grid structures made of stainless steel rope from Hebmetalmesh series are multifunctional and durable, Hebmetalmesh handwoven stainless steel netting was subjected to numerors tests and complies with all applicable standards: as a permanent protective and safety mesh for zoo mesh, animal enclosures, bird aviary, it is absolutely UV- and weather-resistand,100% Hand Woven, Strong, Flexible, Soft, Durable, No Rust, No Corrosion, Useful Life Over 30 Years.
Hebmetalmesh handwoven stainless steel netting has the skin-like characteristics of diaphragm, it can from a plane surfae but can also be tensioned into three-dimensional forms featuring funnel-type, cylin-drical, or spherical shapes.
Introduce Stainless steel mesh for lion enclosure, lion cages, lion barrier nets – 100% Hand Woven, Strong, Flexible, Soft, Durable, No Rust, No Corrosion, Useful Life Over 30 Years
HEBEI KETONG METAL MESH INDUSTRY CO. LTD is professional manufacturer of hand woven stainless steel netting from China, Hebei Metal Mesh Ltd announces to supply custom-made zoo enclosure fence netting, bird control netting and animal fence enclosures netting, and nettings for other applications.
Multiple choices for Stainless steel mesh for lion enclosure, lion cages, lion barrier nets – 100% Hand Woven, Strong, Flexible, Soft, Durable, No Rust, No Corrosion, Useful Life Over 30 Years superiority:
1. Large mesh panel design, for many years, we continuously improve production process, now we can manufacture more than 2,000 sq.ft mesh panel, some specification can manufacture more than 3,000 sq.ft.! And there is no any joint in the middle. Great convenience to users.
2. Ordering production processes, production according to the user’s requirements, you can get every piece of mesh size is suitable for your design, do the zero waste, can most save your cost.
3. We adopt precision mould, ensure mesh size accord with standard, every mesh knot cross woven by hand, ensures that each mesh, each mesh knot never deformation.
4. Installation is concise, because every piece of mesh are manufactured according to the requirement, this will make mesh in line with the framework, make installation is very simple.
5.Material guarantee, Size guarantee, Quality assurance, On time delivery guarantee!
Multiple choices for Stainless steel mesh for lion enclosure, lion cages, lion barrier nets – 100% Hand Woven, Strong, Flexible, Soft, Durable, No Rust, No Corrosion, Useful Life Over 30 Years – hebmetalmesh:
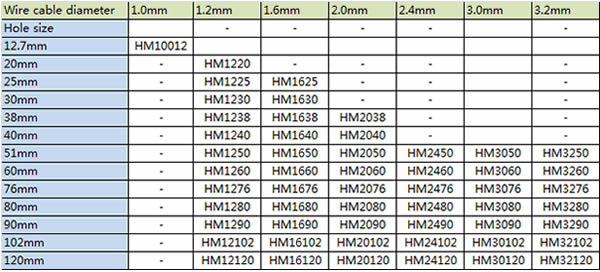
1. 51mm x 51mm x 2.4mm – stainless steel rope mesh HM2450
2. 60mm x 60mm x 2.4mm – stainless steel rope mesh HM2460
3. 51mm x 51mm x 3.2mm – stainless steel rope mesh HM3250
4. 60mm x 60mm x 3.2mm – stainless steel rope mesh HM3260
5. 76mm x 76mm x 3.2mm – stainless steel rope mesh HM3276
6. 80mm x 80mm x 3.2mm – stainless steel rope mesh HM3280
……
Contact us now:
Sales manager: Mr. Steven
Chat with us on website our leave a message;
Sent Email: info@hebmetalmesh.com
Message with Whatsapp: +8615530133907
Message with Wechat: x15530133907